Impact
Economic
Unprecedented Value Creation
Upwing's Subsurface Compression offering provides 2x incremental production from existing natural gas wells at a 70% reduction in production costs with no new drilling.
Upwing clients can expect incremental income ranging from $200K to $2.6M per month per well.
Maximize Asset Value
Upwing's Subsurface Compressor System™ (SCS) creates value by increasing production, increasing recoverable reserves and delaying abandonment.
Previously, only about 60% of the natural gas from onshore reservoirs could be recovered from conventional wells and only about 12% from unconventional wells. When the natural pressure of the gas below the earth diminished, there was no other option but to cap the well.
Now, Upwing's SCS can increase the rate of production from these wells and deplete the natural gas reservoir down to unprecedented levels cost effectively.
Increased Natural Gas Production
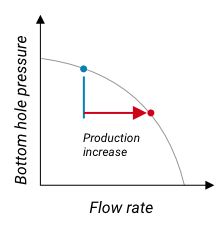
Upwing Subsurface Compressor Systems™ (SCS) increase the gas production by decreasing bottom hole flowing pressure and causing higher reservoir drawdown. Effective drawdown can only be achieved by downhole compression near the perforations, where the gas is denser due to the higher downhole pressure. The effective drawdown increases the production rate significantly, which increases cash flow.
Pressure change
Increased gas velocity
Pressure change

SCS gas well simulations and trials have shown gas production increases ranging from 20% to 200+%. In addition to better gas production, the analysis and trials show that the SCS increases condensate production rates and improves condensate yield. The SCS increases the gas velocity above critical speeds to carry the liquids to the surface. This is more significant in horizontal liquid rich formations, which positively impacts well performance and value.
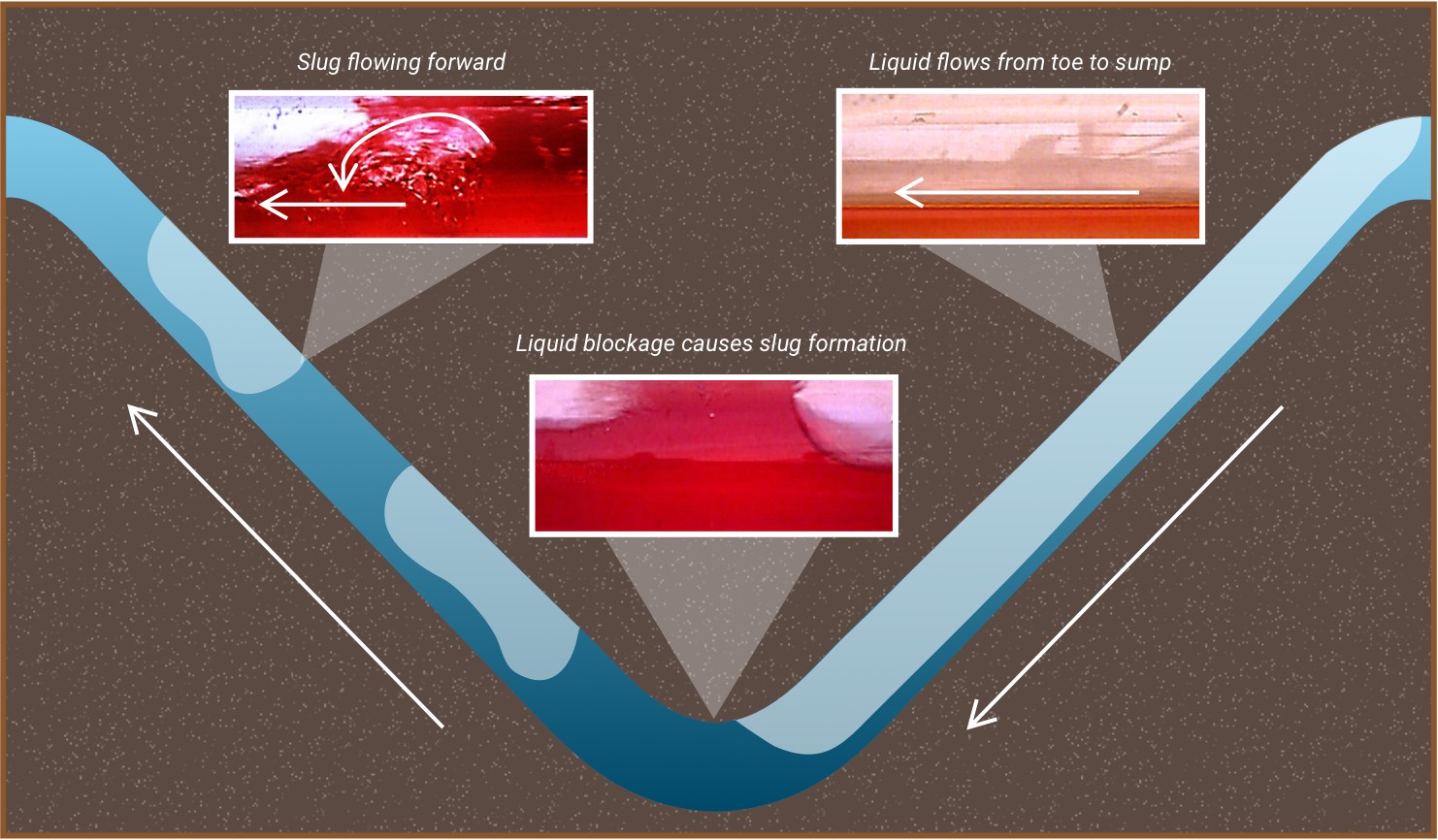
When the gas well is liquid loaded, the back pressure generated by the liquid blockage in the wellbore or pore space in the formation will reduce gas production. The reduced gas flow will reduce gas velocity, which in turn reduces liquid sweeping capability, and allows more liquid accumulation in the gas well or formation.
Increased gas velocity
With the installation of the SCS, the gas velocity at both the intake and discharge of the subsurface compressor will increase. The increased gas velocity can carry more liquid out of the wellbore and reduce the back pressure on the formation caused by the liquid blockage. Once the liquids are removed and the liquid loading is abated, the gas production will increase. The increased gas production will further increase the gas velocity to carry more liquids, thus the virtuous cycle of enacted. Increased gas velocity will improve vertical and horizontal holdup profiles by altering flow behavior and fluid flow distribution, thus enhancing liquid lift efficiency in gas wells.
* Image source: Colorado School of Mines and the University of Tulsa.
Increased Reserves
Drawdown
Increased recoverable reserves
Drawdown

The subsurface compressor aids in the delivery of proven developed reserves and increases the size of undeveloped reserves. The SCS is the only tool that significantly increases the drawdown in the reservoir well beyond any other method utilized today, including wellhead compressors, topside liquid pumps, etc. Lowering the reservoir pressures below what has been possible up until now increases the reserves.
Increased recoverable reserves
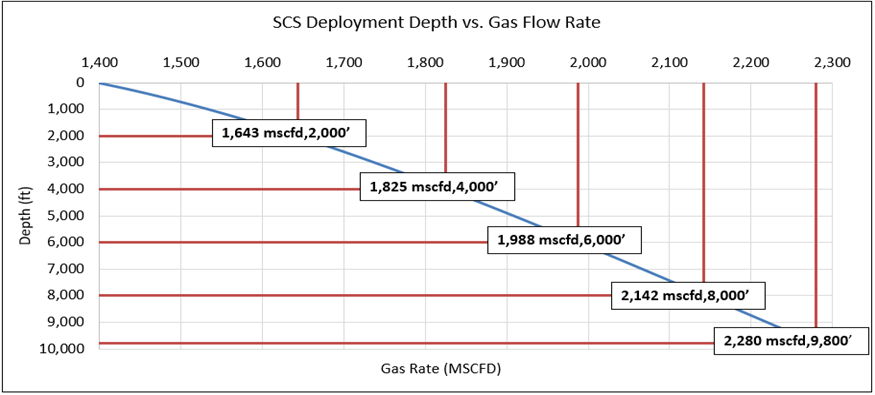
Calculations based on the drawdown from trials show increased recoverable reserves from 20 to 70+%. The graph to the left shows the value of compression as the compressor is positioned closer to the reservoir.
Delayed Abandonment
The SCS can delay the abandonment of gas wells by lowering the abandonment pressure. The delayed abandonment has a direct impact on recoverable reserves. The SCS will provide suction effects at the intake and boosting effects at the discharge.
Suction & boosting effects
Direct impact on recoverable reserves
Suction & boosting effects
- Suction effects - The suction effects with the lower intake pressure will lower the downhole flowing pressure to facilitate the volumetric flow of more gas from the formation into the wellbore.
- Boosting effects - The boosting effects with the higher discharge pressure from the SCS will increase the wellhead pressure to facilitate the flow of gas into the surface gathering system.
With both the suction effects and the boosting effects of the SCS at work, the gas well can still produce gas from the formation under the lowest possible downhole pressure or even vacuum, while forcing the produced gas uphole.
Direct impact on recoverable reserves
With the SCS, downhole pressure does not need to be higher than the wellhead pressure as long as the SCS discharge pressure is high enough to push gas upward. In this case, the effective abandonment pressure is dropped significantly by the SCS, thus delaying abandonment and allowing for the depletion of gas fields.
Superior Value to Drilling and Fracking a New Well
With Upwing's SCS, the initial cost of production is negligible compared to drilling and fracking a new well.

While the 10-year production is similar, the cost of that production is significantly lower with the SCS.
With Upwing's SCS, the cost of production, including service fees is approximately $1.20/mscf, which is about 70% cheaper than the best shale wells with minimal environmental impact.